The synthetic version of the naturally occurring B vitamin folate is called folic acid. Making DNA and other genetic materials are aided by folate. In terms of prenatal health, it is very crucial.

The B vitamin folate, commonly known as vitamin B-9, is found naturally in several foods. Manufacturers add folic acid as a type of folate to vitamin supplements and fortified meals.
What is folic acid?
Typical sources of folic acid, a kind of B vitamin, include dried beans, peas, lentils, oranges, whole-wheat products, liver, asparagus, beets, broccoli, brussels sprouts, and spinach.
In addition to preventing DNA changes that can lead to cancer, folic acid helps your body make and maintain new cells.
Folic acid is a medication used to treat specific kinds of anemia as well as anemia (loss of red blood cells) brought on by folic acid deficiency.
Folic acid may occasionally be used in conjunction with other medications to treat pernicious anemia. Folic acid alone cannot cure pernicious anemia or other anemias unrelated to vitamin B12 deficiency. Take all of your medicines as directed.

Why is folic acid important?
Folate is necessary for several bodily processes.
For instance, it aids in the body’s production of new, healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body. Insufficient production of these can cause anemia, which manifests as weakness, exhaustion, and a pale complexion.
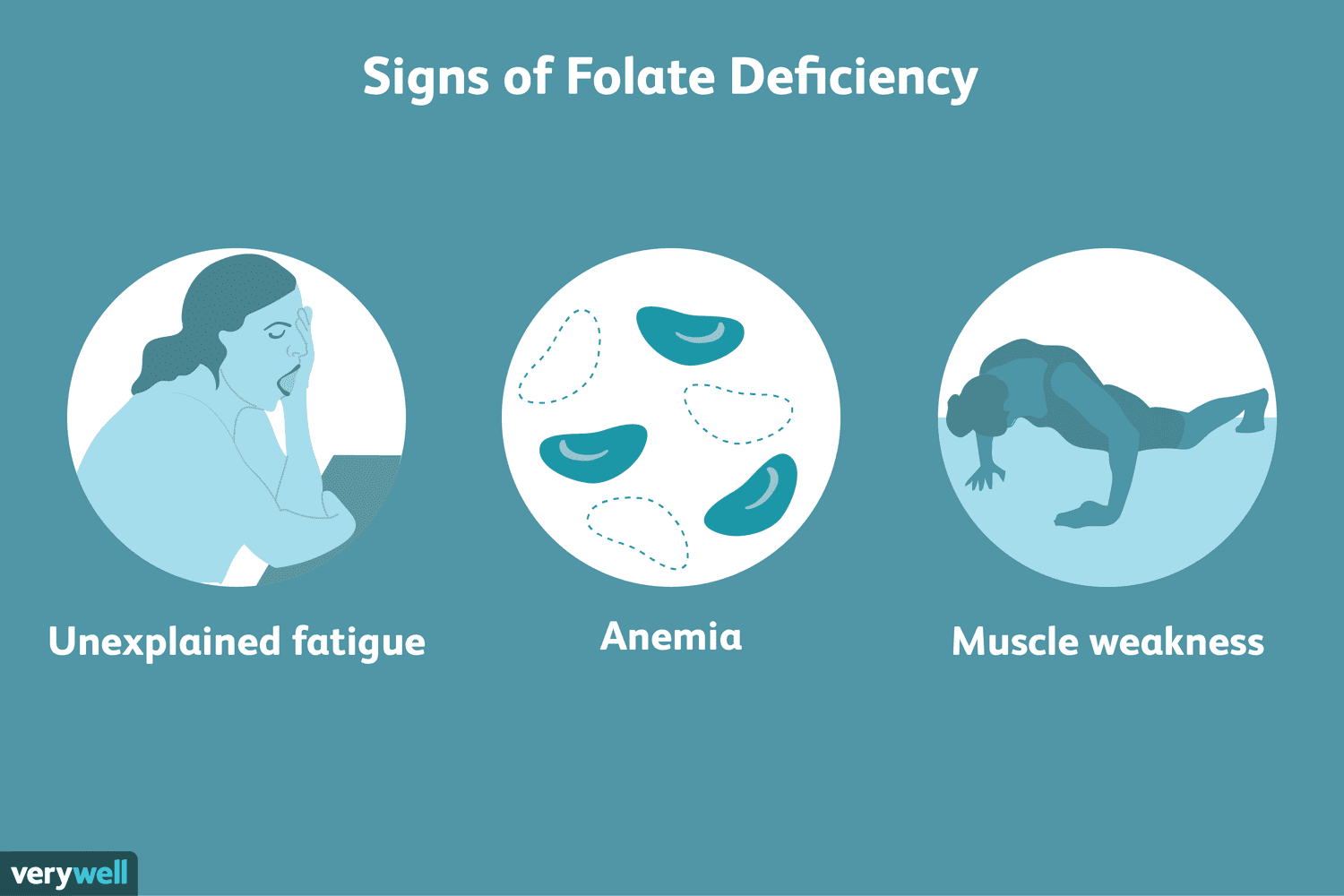
A person can potentially have folate deficiency anemia if they don’t get enough folate.
Folate is required for cell division and essential for the creation and maintenance of DNA and other genetic material.
It’s crucial to consume adequate folate when pregnant. This is because folic acid is essential for embryonic growth, especially in the early stages when it comes to the spinal cord. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mandates that producers add folic acid to enriched bread, pasta, rice, cereals, and other grain products in the United States due to its health significance.
Who should take folic acid?
The majority of individuals consume adequate folate via their diets, and folate deficiency is uncommon in the US. However, taking folic acid supplements can still be advantageous for some people in particular.
Pregnant people
One of the earliest bodily structures to develop in an embryo is the spinal cord, and a folate shortage can cause abnormalities in the spinal cord.
Additionally, it can result in neural tube abnormalities such as spina bifida and anencephaly. The early brain and spine of the embryo are formed by the neural tube.
Along with other things, folic acid may lower the risks of cleft palate, abnormal heartbeat, and premature delivery.

The natural form of dietary folate known as L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate should be taken in doses of 400–800 micrograms (mcg) per day, according to the Office of Women’s Health. 4,000 mcg per day should be taken by anyone who has spina bifida or a family history of neural tube abnormalities.
The recommended daily dose for those who are breastfeeding or chest-feeding is 500 mcg.
Since the FDA mandated the addition of folic acid to food in 1998, fewer infants are being born with abnormalities of the neural tube.
People with mood disorders
Depression may be more common in people with reduced folate levels. According to research, a folate shortage affects as many as 30% of those who suffer from severe depression.
In individuals with depressive illnesses, having blood folate levels less than 6.0 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL) was linked to an increase in suicidal conduct, citing 2021 research.

It’s unclear, though, if folic acid supplementation may lessen depression’s symptoms. It appears from studies from 2019 and 2018 that it might not. To assess the effect of folate on mental disorders, more study is required. A patient with depression should talk to their doctor about taking folate supplements.
Autism spectrum disorder
According to some studies, ingesting folic acid before and throughout the first trimester of pregnancy may lower the baby’s risk of having an autistic spectrum condition (ASD). The study on this topic is conflicting, nevertheless.
For instance, in a 2022 study, researchers discovered that consuming at least 400 of folic acid while pregnant was linked to a lower risk of the fetus having ASD.
On the other side, a 2020 study discovered that excessive folate intake during pregnancy may be linked to ASD in kids.
The putative function of folic acid in this context will require more investigation.
People with rheumatoid arthritis
Folic acid may be prescribed by doctors in conjunction with a methotrexate prescription for rheumatoid arthritis.
For this illness, methotrexate is an effective drug, although it might cause gastrointestinal problems by depleting the body of folate.
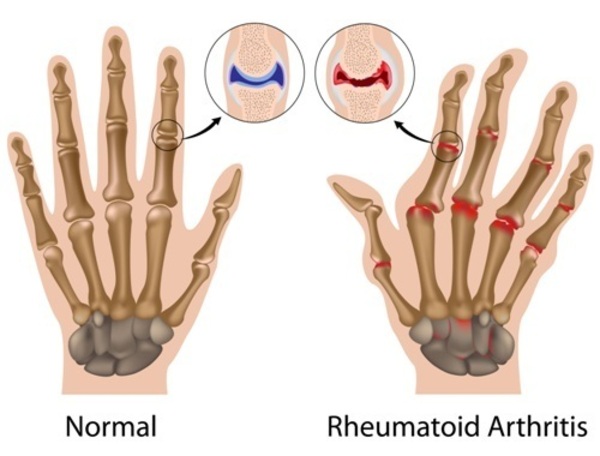
According to studies, taking supplements containing folic acid or L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate might lessen these negative effects by about 79%.
Summary
The synthetic version of the crucial B vitamin folate is called folic acid. While the majority of individuals acquire enough folate through their diets, those who are at risk of deficiency as well as those who are pregnant or may become pregnant may need to take folic acid supplements.
Additional health advantages of folic acid may potentially exist, although there may also be concerns. Folic acid should be avoided by some people. Before adjusting their diet to include more naturally occurring folate or before beginning any folic acid supplements, a person should see their doctor.







